Amblyopia (Lazy Eye) in the Young Generation: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Introduction
Amblyopia, commonly known as "lazy eye," is a vision disorder that affects a significant number of young individuals. It occurs when one eye does not develop properly, leading to reduced vision in that eye. In this article, we will explore the causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for amblyopia in the young generation.
Understanding Amblyopia
Amblyopia occurs when the brain favors one eye over the other. This preference for one eye leads to reduced vision in the "lazy" eye, as the brain relies more on the dominant eye for visual input. If left untreated, amblyopia can result in permanent vision impairment.
Causes of Amblyopia
Amblyopia can have various underlying causes, including:
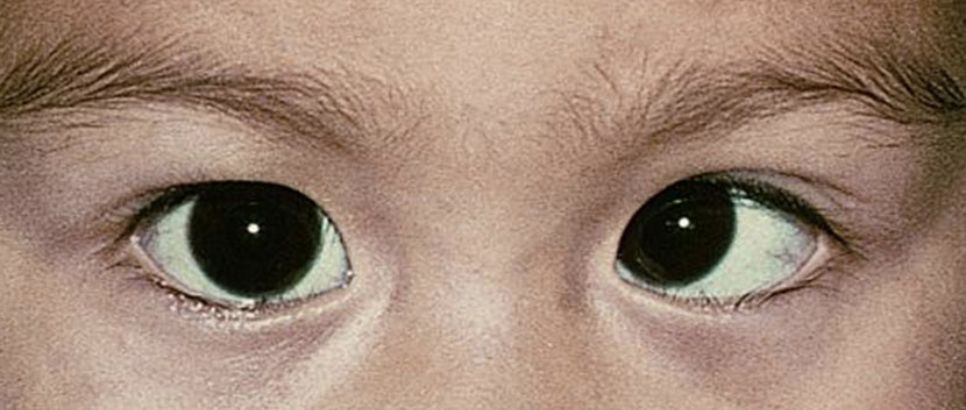
Strabismus: Strabismus is a condition where the eyes are misaligned, meaning they do not focus on the same point simultaneously. This misalignment can lead to amblyopia in the weaker eye.
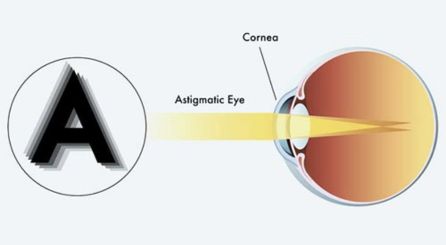
Refractive Errors: A significant difference in the refractive error (such as nearsightedness, farsightedness, or astigmatism) between the two eyes can cause amblyopia in the eye with the more significant refractive error.
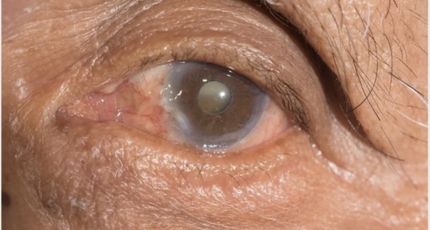
Deprivation Amblyopia:Deprivation Amblyopia: This occurs when something physically obstructs vision in one eye during the critical early childhood development phase. Examples include congenital cataracts or a droopy eyelid.
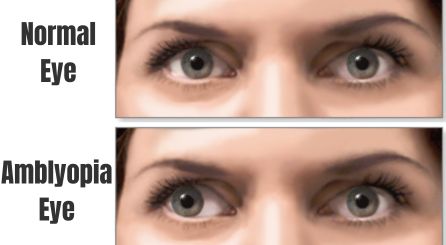

Diagnosis of Amblyopia
Early detection of amblyopia is crucial for effective treatment. Children should undergo comprehensive eye exams starting at a young age. Common diagnostic methods include:
Visual Acuity Testing: This assesses how well each eye can see by reading letters from an eye chart.
Cover Test: This test checks for eye misalignment (strabismus).
Refraction: Measuring the eye's refractive error to detect significant differences between the two eyes.
Pupil Response: Evaluating how the pupil responds to light can help diagnose deprivation amblyopia.
Treatment for Amblyopia
The goal of amblyopia treatment is to strengthen the "lazy" eye and improve visual acuity. Treatment options include:
Eyeglasses or Contact Lenses: Correcting refractive errors with prescription eyeglasses or contact lenses can help improve vision in the weaker eye.
Eye Patching: Covering the stronger eye with an eye patch for a specified period each day forces the brain to rely on the "lazy" eye, stimulating its development.
Atropine Drops: Instead of patching, some children may use atropine eye drops in the stronger eye to blur vision temporarily, encouraging the use of the "lazy" eye.
Vision Therapy: Vision therapy involves exercises and activities to improve eye coordination and visual processing skills.
Surgery: In cases of strabismus or other physical obstructions, surgery may be necessary to align the eyes or remove obstacles.
Conclusion
Amblyopia, or "lazy eye," is a common vision disorder among young individuals that can lead to permanent vision impairment if left untreated. Early detection through regular eye exams and prompt intervention is essential for successful treatment. With the right approach, including eyeglasses, eye patching, or other therapies, many young individuals with amblyopia can significantly improve their vision and lead a life with clear and healthy eyesight. If you suspect amblyopia in yourself or a loved one, consult with an eye care specialist for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan.
You Might Also Like
Popular Posts
-
 Conjunctivitis Condi...
Conjunctivitis Condi...3 June 2023
-
 Glaucoma: Silent Thi...
Glaucoma: Silent Thi...26 Mar 2023
-
 Cataracts: Your eye....
Cataracts: Your eye....17 Jan 2023
About Us
The Eye Clinic brings all the modern equipment & experienced doctors providing high-quality eye care affordably.